What is Overtime Pay: Policies, Regulations, and Best Practices

In fact, if an employer willfully or repeatedly violates overtime requirements, they will be subject to a civil money penalty of up to $1,000 for each violation. Overtime Laws in the States – provides a clickable map that informs what the overtime how much is overtime pay laws are in each state. Questions and Answers about Overtime Pay – Answers questions ranging from when overtime pay is due and how many hours an employee may work. For a job position to be considered a ‘learned or artistic profession,’ an employee must have a specialized college degree or pursue other paths of academic study.
- Using the one-and-a-half rule of thumb, an employer would calculate overtime pay by multiplying a worker’s hourly rate by 1.5 and then multiplying the result by the number of overtime hours they worked.
- With Congressional Republicans having passed a budget resolution, one of the tax provisions certain to be discussed in federal budget deliberations will be President Trump’s expressed priority to exempt overtime pay from taxation.
- To help you navigate this unfolding story, we’ve put together some FAQs based on the latest chatter and insights.
- The IRS would have to modify tax forms for employers to report information on workers’ hours and delineate between regular wages and overtime earnings.
- For every hour of overtime, employees get their regular hourly rate, 1.5 times.
- The standard salary level that currently exempts executive, administrative, and professional employees is $844/week or $43,888 annually for full-time staff.
What are the Different Types of Overtime Pay?
Exempting overtime from taxation would also make the tax code more complex, both for tax agencies to administer and for employers to follow. At the federal level, Internal Revenue Service (IRS) reporting requirements do not ask employers or employees to distinguish between regular pay and overtime pay. The IRS would have to modify tax forms for employers to report information on workers’ hours and delineate between regular wages and overtime earnings. State tax agencies would also need to revise accounting systems and potentially hire new staff to maintain accurate overtime records. Overtime exists to disincentivize employers from overworking their employees. If a boss asks workers to put in more than 40 hours in a week, they must pay a premium—usually 1.5 times their regular rate of pay—for those excess hours.
No tax on overtime is another gimmick that would do more harm than good

Whether that’s over a typical eight-hour workday or a 40-hour workweek, the federal government has made it mandatory to compensate all non-exempt employees. This is important as it protects workers and rewards them for the additional time they spend supporting your business. Their employer could pay them about $13.75 per hour, and if they continued to work that 60-hour work week year-round, they’d get about $4,000 more in after-tax pay, while costing the employer nothing in additional compensation.
No Tax on Overtime Would Reduce Federal Revenues
It was a policy choice made only after fierce struggle, organizing, and advocacy by workers who labored 60–80 hours a week in difficult and dangerous jobs. The federal overtime laws require employers to compensate employees at least time and a half or double time for the extra time they put in. Time and a half is equivalent to more than 50% of an employee’s standard wage. For every hour of overtime, employees get their regular hourly rate, 1.5 times. Overtime is a regulation of organized labor designed to help improve the working hours and working conditions of workers, and prevent exploitation by their employers. Under the United State’s current overtime rules, employers must pay their employees “time-and-a-half” wages (one and a half times the employee’s regular hourly wage) for all hours worked over the national overtime limit of 40 hours per week.
- Employers might also restructure pay to favor bonuses or overtime over hiring additional staff, reducing job opportunities and encouraging overwork.
- Annual overtime is the total number of extra hours an employee works outside their normally scheduled working time in a year.
- The overtime rules enacted were designed to address several of the main problems Roosevelt sought to address with his labor reforms – lack of jobs, and the exploitation of those who had jobs.
- No tax on overtime would particularly benefit employers currently misclassifying staff as exempt from overtime.
- As long as a fixed and regularly recurring schedule is established, employees should receive the overtime rate owed to them.
- There are many ways to do this; however, manually tracking and calculating overtime hours is a dangerous game.
While we take all precautions to ensure that the data on this site is correct and up-to-date, we cannot be held liable for the accuracy of Car Dealership Accounting the labor law data we present. Applying the current-policy baseline would not only be fiscally irresponsible in terms of this year’s tax debate, but it would set a dangerous precedent for the future. Fully extending the TCJA would cost approximately $5.0 trillion, while other elements of the Republican tax agenda also have large price tags over ten years. Nationally, only approximately 6 percent of employed individuals reported that they typically worked overtime in 2024. See the returns you’ll get from an automated and more efficient hourly workforce. A network of state and local organizations improving workers’ lives through research and advocacy.
Estate, Inheritance, and Gift Taxes in Europe, 2025

As a result, failure to comply with the FLSA rules can cost employers double the amount of paying their employees overtime in the first place. Violations committed on purpose can also result in substantial fines and the threat of imprisonment if the employer is a repeat offender. If an employee’s job is classified as an Outside Sales position, then their main duties are making sales or taking orders outside their company’s main workplace. These employees can be paid either a salary or commission-based structure, but they need to spend more than 20% of their time performing work other than sales to fall under this category. The FLSA applies on a workweek basis and considers that a worker’s week is a fixed and regularly cyclical period of 168 hours, which are seven consecutive 24-hour periods. The workweek doesn’t have to coincide with the calendar week, and it can begin on any day and at any hour of the day.
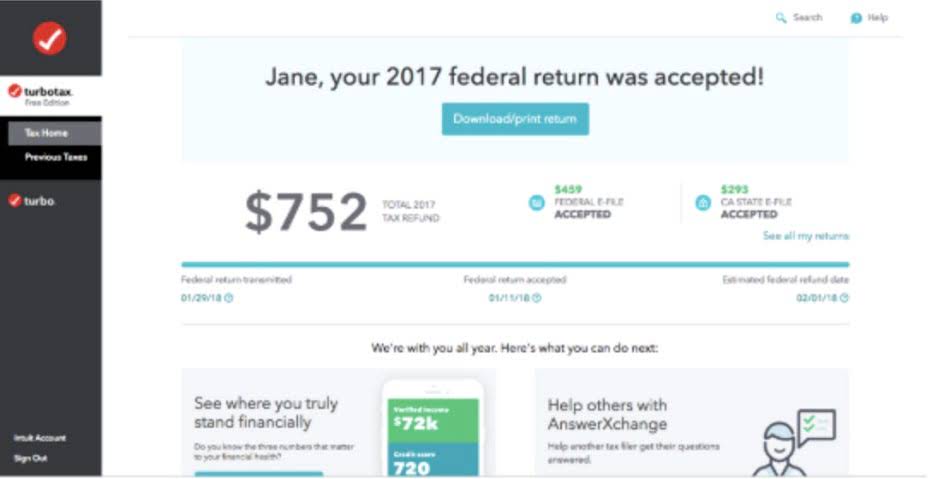
From Google to Nectar: How Cassidy Gonzalez is redefining employee engagement

Before overtime regulations were contribution margin introduced in 1938, working hours were often exceedingly long and brutal for the average American worker. Blue-collar employees in industrial settings often worked hours a day – many employers took advantage of high poverty rates to force their employees to work around the clock just to earn enough money to keep food on the table. As part of a group of tax proposals, Republican leaders recently called for eliminating taxes on overtime pay. Excluding overtime compensation from federal taxes would create a new tax expenditure — also known as a tax break — that would reduce federal revenues and make the U.S. tax system more complex. Here, we review how much no tax on overtime could impact federal tax receipts and deficits, as well as its effect on fairness within the federal tax system. Workforce.com’s Payroll platform makes the hassle of recording, calculating, and paying overtime much easier.

















